Capacitor Android Documentation
Capacitor features a native Android runtime that enables developers to communicate between JavaScript and Native Java for Android code.
Capacitor Android apps are configured and managed through Android Studio (generally). Follow these guides for more information on each topic:
Getting Started
Developing Android apps requires some Android SDK dependencies to be installed. Make sure to install the Android SDK Tools (26.0.1 or greater required), and a version of the Android SDK Platforms for API 21 or greater.
You can install these easily by opening Android Studio, and going to Tools -> Android -> SDK Manager from the top menu bar:
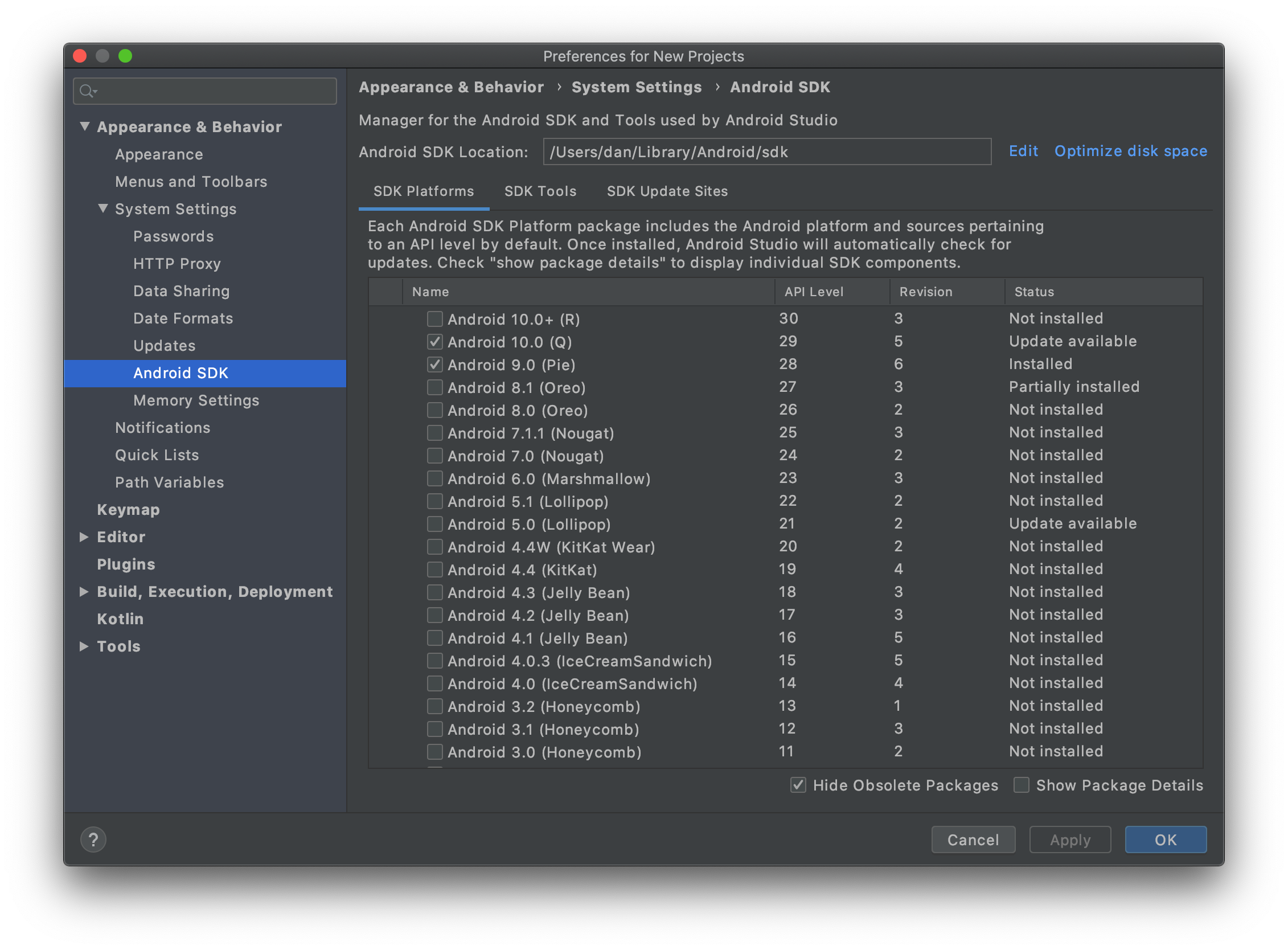
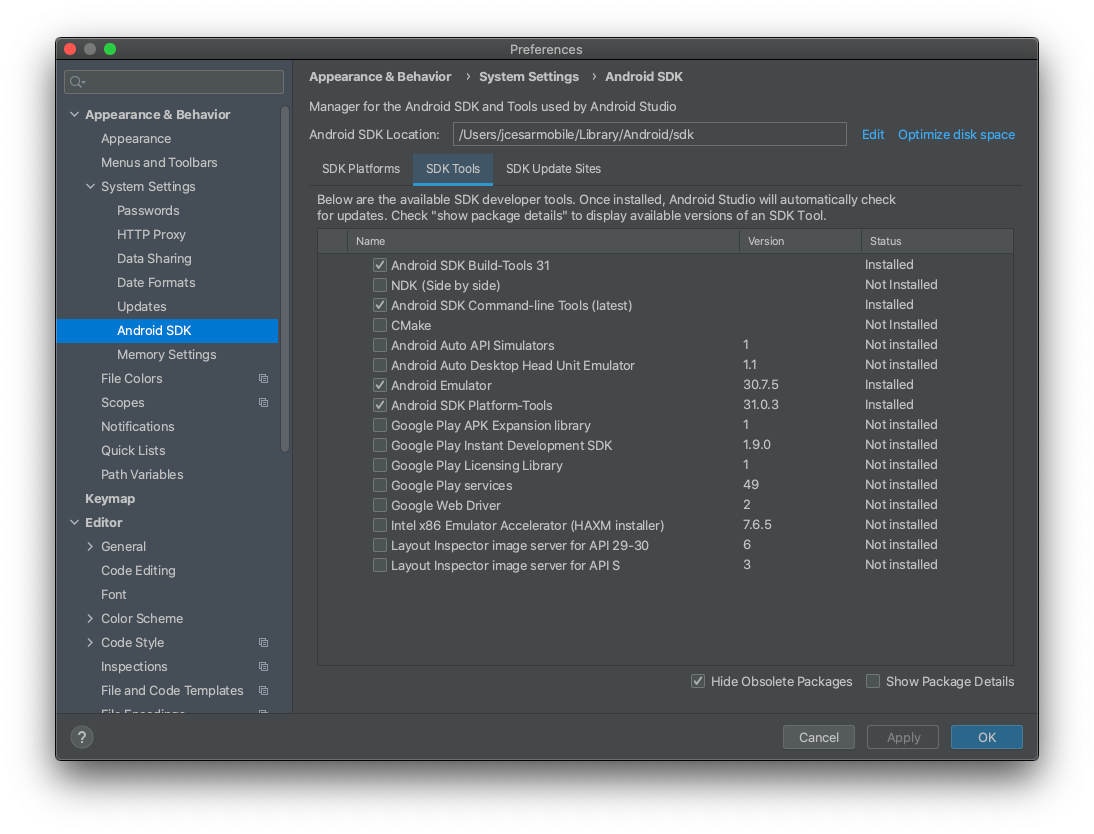
Creating Android Project
By default, an Android project is created for every Capacitor project. If you are adding Capacitor to an existing project, you can manually add the Android project using:
npx cap add android
npx cap sync
The sync command updates dependencies, and copies any web assets to your project. You can also run:
npx cap copy
To copy web assets only, which is faster if you know you don't need to update native dependencies.
Opening Android Project
To open the project in Android Studio, run:
npx cap open android
Running Your App
Note: Currently to use an Android Emulator you must use a system image of at least Android version 7.0 on API 24. This is due to the System WebView version not being able to be updated on emulators. Physical devices should work as low as Android 5.0 (API 21) as long as their System WebView is updated.
Once Android Studio is open, you should be able to run your app on a device or emulator. Click Run or Debug:
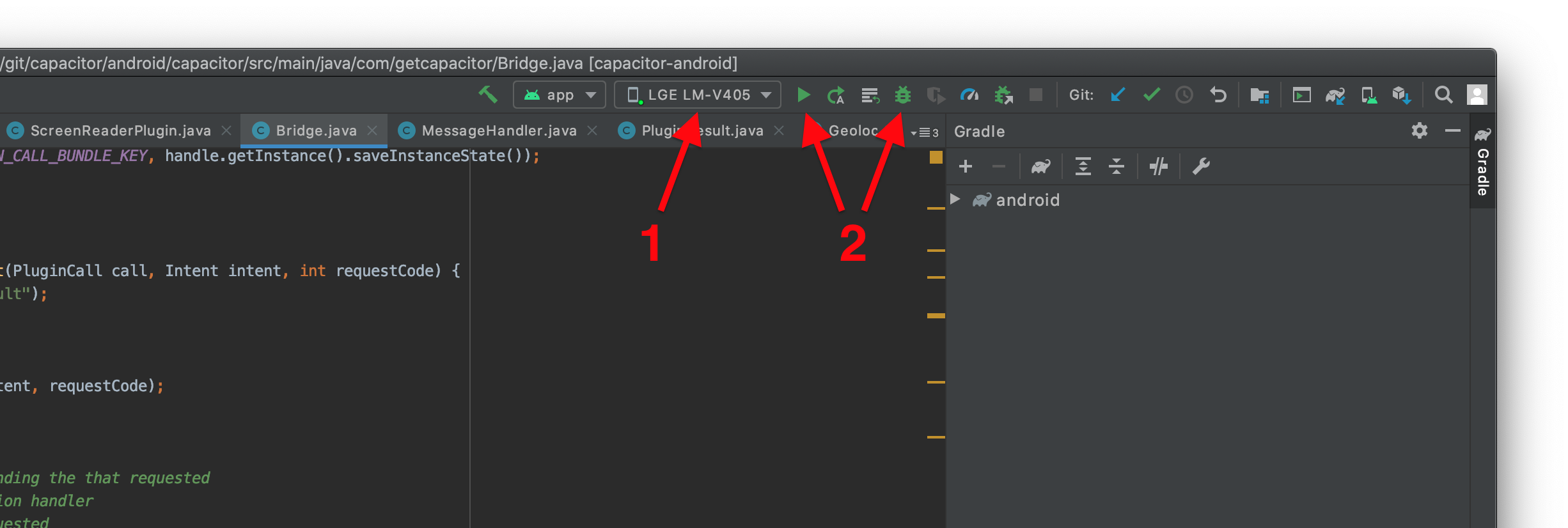
Troubleshooting
If you encountered any issue above, please let us know by filing an issue on the repo, and then consult the Troubleshooting Android page for solutions to common Android problems.
Next Steps
If your app ran you are now ready to continue developing and building your app. Use the various APIs available, Capacitor or Cordova plugins, or custom native code to build out the rest of your app.
Further Reading
Follow these Android-specific guides for more information on setting permissions for your app, updating dependencies, building plugins, and more: